Abstract
We address the over-constrained planning problem in semi-static environments. The planning objective is to find a best-effort solution that avoids all hard constraint regions while minimally traversing the least risky areas. Conventional methods often rely on pre-defined area costs, limiting generalizations. Further, the spatial continuity of navigation spaces makes it difficult to identify regions that are passable without overestimation. To overcome these challenges, we propose SuReNav, a superpixel graph-based constraint relaxation and navigation method that imitates human-like safe and efficient navigation. Our framework consists of three components: 1) superpixel graph map generation with regional constraints, 2) regional-constraint relaxation using graph neural network trained on human demonstrations for safe and efficient navigation, and 3) interleaving relaxation, planning, and execution for complete navigation. We evaluate our method against state-of-the-art baselines on 2D semantic maps and 3D maps from OpenStreetMap, achieving the highest human-likeness score of complete navigation while maintaining a balanced trade-off between efficiency and safety. We finally demonstrate its scalability and generalization performance in real-world urban navigation with a quadruped robot, Spot.
Overall Architecture
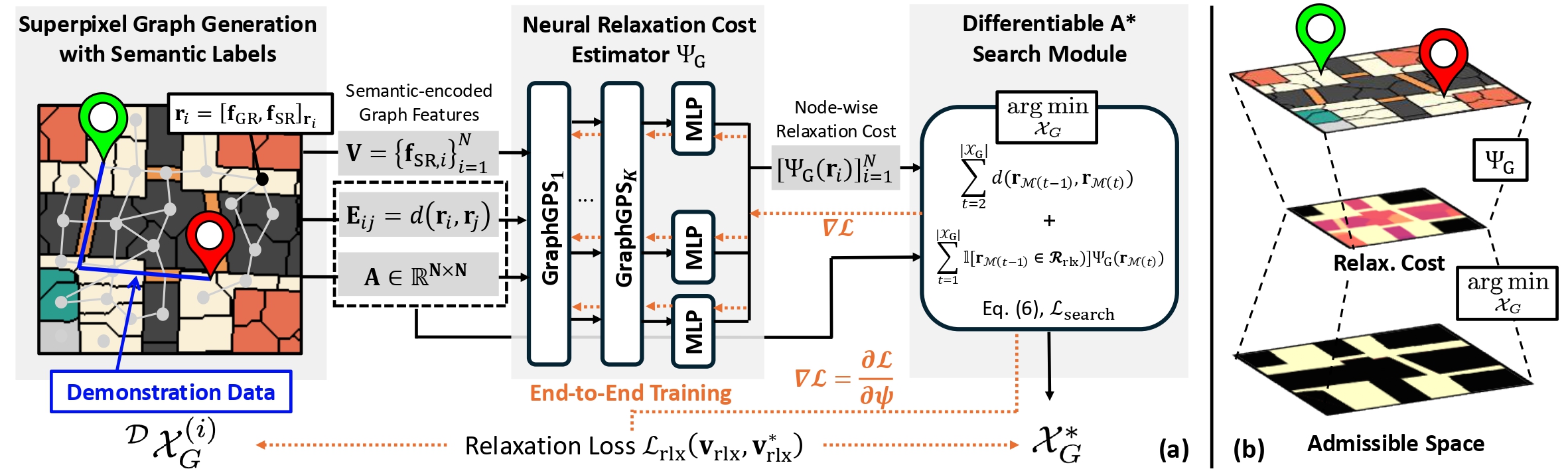
Overview architecture of SuReNav that automatically relaxes regional constraints while planning a graph path $\mathcal{X}_G$ in semi-static navigation environment. (a) In the training phase, SuReNav generates a superpixel graph from a 2-dimensional map with safety-relevant semantic features. A neural relaxation cost estimator $\Psi_G$ then computes a node-wise relaxation cost, which is incorporated as an optimization term in a differentiable search process. This enables end-to-end training of the model from human demonstrations. (b) During the planning phase, the estimator generates node-wise relaxation costs, and a discrete graph search process selects regions to relax, inducing an admissible space to facilitate path planning.
Qualitative Results
Quantitative Results
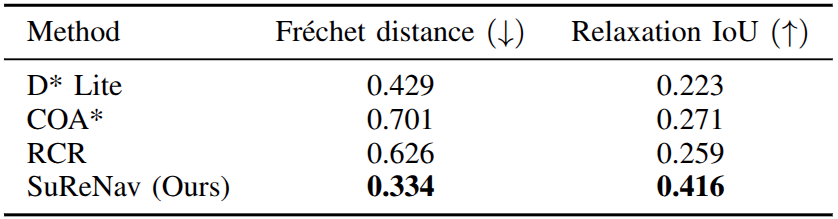
Human-likeness evaluation results on 2D semantic maps. SuReNav achieves the highest human-likeness score compared to baselines.
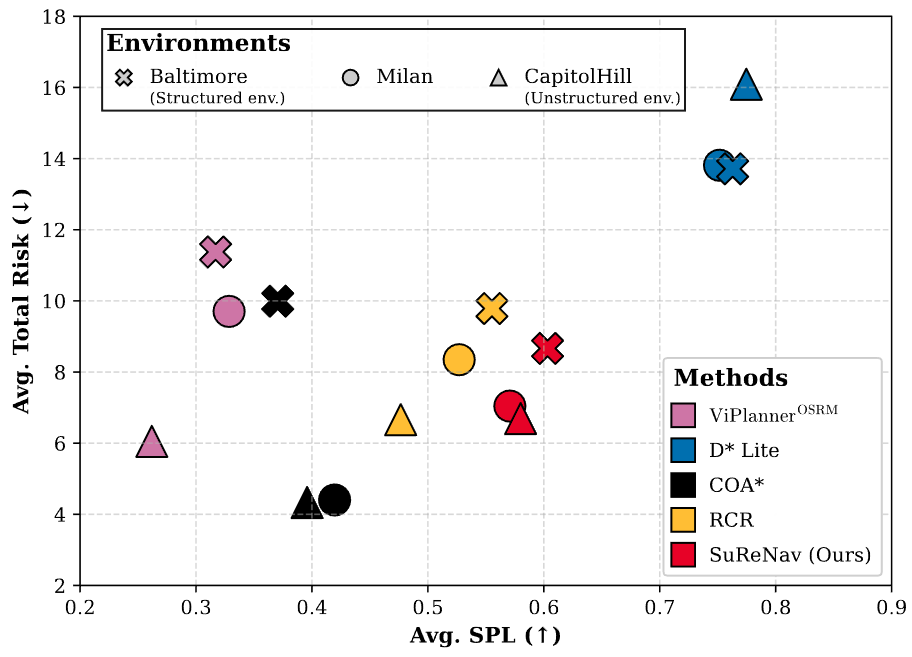
Safety-efficiency trade-off evaluation results on 2D semantic maps and 3D OSM maps. SuReNav demonstrates balanced trade-off between safety and efficiency compared to baselines.
BibTeX
@article{koh2026surenav,
title={SuReNav: Superpixel Graph-based Constraint Relaxation for Navigation in Over-constrained Environments},
author={Koh, Keonyoung and Jung, Moonkyeong and Lee, Seungsup and Park, Daehyung},
journal={Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)},
year={2026}
}